- Home
- PATIENT INFORMATION
- PROCEDURES
- MEET US
- SURGICAL INSTRUCTIONS
- REFERRING DOCTORS
- CONTACT US

What Is An Impacted Tooth?
Types Of Impactions
Why Should I Have My Wisdom Teeth Removed?
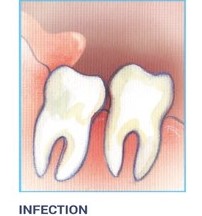
Infection:
The most frequent clinical problem we see is pericoronitis, (a localized gum infection). Without enough room for total eruption, the gum tissue around the wisdom tooth can become irritated and infected, resulting in recurrent pain, swelling, and problems with chewing and/or swallowing.
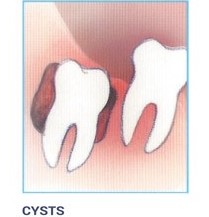
Cyst Formation:
Non-infectious diseases may also arise in association with an impacted wisdom tooth. Cysts are fluid-filled "balloons" inside the jawbone that develop as a result of impacted teeth and slowly expand destroying adjacent jawbone and occasionally teeth. They can be very difficult to treat if your wisdom teeth are not removed in your teenage years. Although rare, tumors can be associated with the delayed removal of wisdom teeth.
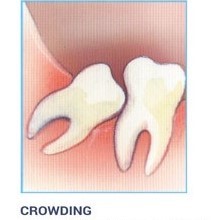
Possible Crowding:
Impacted wisdom teeth may contribute to crowding of your teeth. This is most noticeable with the front teeth, primarily the lower front teeth and is most commonly seen after a patient has had braces. There are a number of factors that cause teeth to crowd after braces or in early adulthood. Retained, impacted wisdom teeth may be a contributing factor. Unless you have an active problem when you see the oral surgeon, the reason for removal is primarily to prevent long-term damage to your teeth, gums and jawbone.
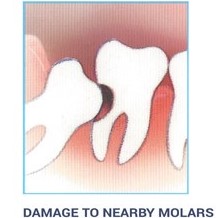
Damage to Adjacent Teeth:
If there is inadequate room to clean around the wisdom tooth, the tooth directly in front, the second molar, can be adversely affected resulting in gum disease, bone loss around the tooth, and/or decay.
What Happens On The Day They Are Removed?
What Happens Afterwards – What Will I Feel Like?
Are There Any Problems?
Damage to Sensory Nerve:
A primary concern is a nerve within the lower jawbone that supplies feeling to the lower lip, chin, and tongue. This nerve is frequently very close to the roots of the lower wisdom teeth. Having these teeth out between the ages of 12 and 18 usually provides shorter roots so that the nerve is not so close to the roots of these teeth. Occasionally, when the teeth are removed, and especially in older patients, the nerve can become injured. When local anesthesia wears off, you may experience a tingling or numbing sensation in the lower lip, chin, or tongue. Should this occur, it is usually temporary and will resolve gradually over a period of weeks or months. On rare occasions it can result in a permanent alteration of sensation similar to having local anesthesia. We feel that you should be aware of this possibility before consenting to surgery.
Sinus Communication:
The upper wisdom teeth are situated close to your sinuses, and their removal can result in an opening between your mouth and the sinus. Once again, if the teeth are removed at an early age, the root formation is minimal, and this complication is very unlikely. However, if it does occur, it will usually close spontaneously, but we may give you special instructions to follow, such as avoid blowing your nose for two or three days following the surgery. You can wipe your nose, but don't blow your nose. If you have to sneeze, you should sneeze with an open mouth into a tissue. Pressure should not be created in the sinus area, which may dislodge the healing blood clot. If you sense this condition occurring after the surgery, please contact the office. An additional procedure may RARELY be necessary to close the opening.
Dry Sockets:
Dry sockets continue to be the most common problem people experience following dental surgery. They arise due to premature loss of a blood clot in the empty tooth socket. This seems to occur with greater frequency in people who smoke or are taking birth control pills. While both jaws can be affected, they usually occur in the lower jaw on the third to fifth day. They cause a deep, dull, continuous aching on the affected side(s). Patients may first notice the pain starting in the ear radiating down towards the chin.
The symptoms frequently begin in the middle of the night, and your pain medication regimen may not help. Treatment can involve changing your prescription. Occasionally it is helpful to place a medicated dressing in the empty tooth socket. This will help decrease the pain and protect the socket from food particles. The effectiveness in alleviating the pain lasts for 24-48 hours and may require dressing changes every day or two, for five to seven days. Dressings usually are removed when you have been pain free for 2 to 3 days.
The dressing doesn't aid in healing. The only reason to place a dressing is for pain control. If medication is controlling the pain, the socket will heal without a dressing. Following removal of the dressing, an irrigation device may be provided to help you to keep food particles from lodging in the extraction site.
Infection:
Occasionally, post-operative infections occur. This usually requires an office visit and clinical examination. Many times, just placing you on an antibiotic for one week will take care of the infection. If it persists, the area will have to be drained and cleaned. Other temporary problems you may experience in the post-operative period include stiffness of the jaws, chafing around the corners of your lips, facial bruising, and blood oozing from the extraction sites. The post-operative instruction sheet we will provide should answer many of the questions related to these more common concerns. If not, don't hesitate to call the office.
What Does The Procedure Cost And Is It Covered By Insurance?
What If I Have Questions Before Surgery?
Oral Examination
Removal
2016 © Greater Houston Oral & Facial Surgery. ALL Rights Reserved.
Developed By : BRON SOFTWARE